Rim Size Designation
Example tractor rim W 14L x 20
W rim profile code (single well)
14 rim width in inches
L flange height code
20 rim diameter in inches
Example tractor rim DW 12 x 38
DW = rim profile code (double well)
12 = rim width in inches
38 = rim diameter in inches
| Flange height axles |
| 25.4mm |
L |
| 19.7mm |
K |
| 17.3mm |
J |
| 22.2mm |
F |
| 19.8mm |
E |
| 17.5mm |
D |
| Rim prolilecodes |
| welJshape |
W |
| doubleweD shape |
DW |
Offset
All wheels have a given offset (0) which not only provides for the necessary brake drum space, but which also determines track width, performance charac¬teristics and wheel bearing load. On dual assemblies, it also influences the spacing.
Fixed wheels have a fixed offset, adjustable wheels have a variable offset.
Tyre fitters and mechanics must therefore ensure that :
a. specific vehicles are fitted with the correct offset wheel
b. wheels with different offsets are not mixed on the same axle.
Wheel offsets can be positive, negative or zero. The offset is defined as the distance from the rim centre to the inside face of the disc (against the hub) and is called positive whenever this inside face is located outside of the centreline, negative when located inside, zero when matching the centreline exactly.

Rims and Tyre
Tyres are designed and moulded to fit a certain rim diameter, rim width and flange contour. A tyre which is fitted onto a wrong size and/or type rim will therefore be forced into an unnatural shape and inadequately seated.
Consequences of such a mismounting could be high pressure leak, bead seat and/or flange area erosion and premature bead area fatigue.
It should therefore be mandatory to always double check and make sure that rim width and flange height dimensions in particular are correct. For diameter tolerance checks, a special ball tape is required.
Whenever a new tyre is fitted, the rim must be cleaned, particularly in the bead seat area. All dirt and rust particles must be brushed away and the complete rim should be repainted. To minimize rim corrosion, it is recommended to regularly drain the air supply system.
A wheel essentially consists of two parts : the rim and the disc
The rim is designed to receive the tyre. Its flanges keep the beads in place when the tyre is inflated. The two seats, usually inclined at 5 degrees to improve the fitting, can be either smooth or knurled (which avoids tyre slippage on the rim). The drop centre is needed to enable mounting and dismounting of the tyre and its shape reinforces the rim structure.
The disc permits the attachment of the wheel to the vehicle hub. Its configuration is dependent on the type of hub.
The disc and the rim of the rear tractor tyre are usually welded or riveted together permanently. Certain wheel types, however, have disconnecting discs and rims to allow the tractor user to modify the wheel track in function of specific cultures or the use of special implements (see: Wheels with adjustable centres)
Whereas all rim parameters have been established by the ETRTO association, no such arrangement has been made with regard to the discs, the characteristics of which vary from one tractor and/or wheel manufacturer to another.
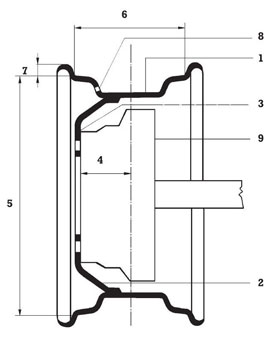
- Drop centre
- Disc
- Huh contact face
- Offset
- Rim diameter
- Rim width
- Rim flange height
- Valve hole
- Huh/brake drum
Note : Rim diameters can only be accurately measured by means of a special ball tape.